|
[See also Blocking on Multiple RTOS Objects]
The FreeRTOS tutorial book
provides additional information on queues, binary semaphores, mutexes, counting
semaphores and recursive semaphores, along with simple worked examples in a set of accompanying example projects.
FreeRTOS Mutexes
Mutexes are binary semaphores that include a priority inheritance mechanism. Whereas binary semaphores
are the better choice for implementing synchronisation (between tasks or between tasks and an interrupt), mutexes are the better choice for implementing
simple mutual exclusion (hence 'MUT'ual 'EX'clusion).
When used for mutual exclusion the mutex acts like a token that is used to guard a resource. When a task wishes to access the resource it must first
obtain ('take') the token. When it has finished with the resource it must 'give' the token back - allowing other tasks the opportunity to access the
same resource.
Mutexes use the same semaphore access API functions so also permit a block time to be specified. The block time indicates the maximum number of 'ticks'
that a task should enter the Blocked state when attempting to 'take' a mutex if the mutex is not immediately available. Unlike binary semaphores
however - mutexes employ priority inheritance. This means that if a high priority task blocks while attempting to obtain a mutex (token) that is
currently held by a lower priority task, then the priority of the task holding the token is temporarily raised to that of the blocking task. This mechanism
is designed to ensure the higher priority task is kept in the blocked state for the shortest time possible, and in so doing minimise the 'priority inversion'
that has already occurred.
Priority inheritance does not cure priority inversion! It just minimises its effect in some situations. Hard real time applications should be designed such
that priority inversion does not happen in the first place.
Mutexes should not be used from an interrupt because:
-
They include a priority inheritance mechanism which only makes sense if
the mutex is given and taken from a task, not an interrupt.
-
An interrupt cannot block to wait for a resource that is guarded by a
mutex to become available.
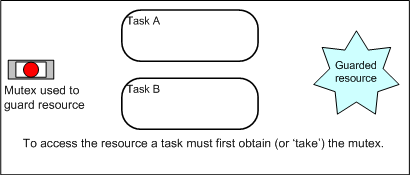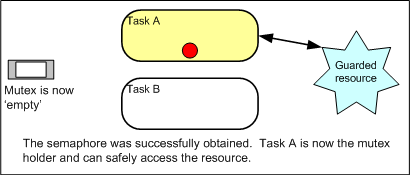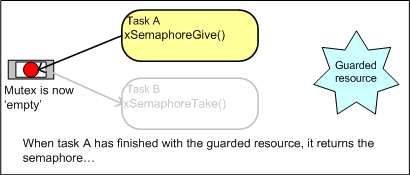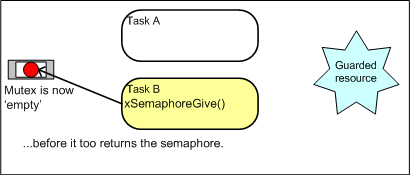 Using a mutex to guard access to a shared resource. Using a mutex to guard access to a shared resource.
Copyright (C) Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
|